Online Grapher
Hyperglossary
Unit 3 Polynomials and Rational Functions
![]() Graphing Calculator Skills needed for this chapter.
Graphing Calculator Skills needed for this chapter.
Section 3.4 Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
This section explores one of the most important and famous algebraic theorems.
Objectives: You should be able to:
-
 Understand the concept of
multiplicity
Understand the concept of
multiplicity
-
 Find the exact zeros
of a polynomial
Find the exact zeros
of a polynomial
-
Basic steps( assuming one at least one
rational):
- Graph
- Check graph and table feature for any integer or rational zeros that can be easily verified
- List all possible rational zeros, check graph for these.
-
Use table feature on ASK to substitute all possible rational zeros.

- Use synthetic division to reduce equation to a more solvable one
- Solve reduced equation, remembering that imaginary and irrational zeros come in pairs.
-
 Find
the least polynomial given the
zeros
Find
the least polynomial given the
zeros
Section 3.5 Rational functions .
This section explores functions in the form f(x) = p(x)/q(x). For help on graphing look at section 3.6 in the text and on this page below.You should be able to:
-
 Find the
Domain and range of rational
functions.
Find the
Domain and range of rational
functions.
This can be done easiest with the graphics calculator.
y = 1/x
The x values in the range are from negative infinity to positive infinity excluding zero. This is the Domain written in interval notation as (-oo , 0) U (0, oo) . The range is also all the reals except 0 written as , (-oo , 0) U (0, oo) .
y = (2x+1) / ( x+1)
The domain is all the reals except 0 and the range is all the reals except 2.
D= (-oo , 0) U (0, oo) R = (-oo , 2) U (2, oo).
-
 Find the
Asymptotes of rational
functions using algrbaic rules and with the calculator..
Find the
Asymptotes of rational
functions using algrbaic rules and with the calculator..
- There are three possible type of asymptotes to rational functions, vertical, horizontal and slant.
-
 This function has both a horizontal and a vertical asymptote.
This function has both a horizontal and a vertical asymptote.
 This function has a slant asymptote.
This function has a slant asymptote.
- To find the asymptote,use long division to divide the denominator into the numerator. The quotient without the remainder is the slant asymptote when degree of numerator is 1 more than that of denominator.
Section 3.6 Graphing Rational Functions
This section explores the graphs of rational functions.
You should be able to find the following using the graphics calculator along with a combination of algebraic methods:
-
 x and y intercepts
x and y intercepts
-
 Symmetry
Symmetry
-
 Horizontal, Vertical, and Slant
asymptotes
Horizontal, Vertical, and Slant
asymptotes
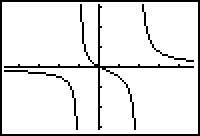 The function on the left has vertical asymptotes at x = 2 and
x = -1. It has horizontal asymptote at y = 0.
The function on the left has vertical asymptotes at x = 2 and
x = -1. It has horizontal asymptote at y = 0.
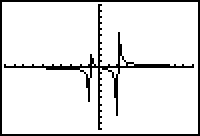
Use the excellent examples in the text to help you with this section. In graphing rational functions the author suggests using DOT MODE on the calculator. This works for some functions and eliminates the "false asymptote" that the calculator can give you. However a better graph can be obtained in many functions using ZOOM ZDecimal after pressing GRAPH. Another alternative is to double the ZDecimal Window as shown.
 |
 |
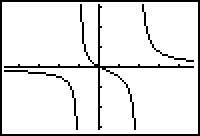 |
 |
| Using ZOOM 6 | Using Dot mode | Using ZDecimal | Zdecimal doubled |
|
©Joan Bookbinder 1998 -2002 All rights reserved